What 400 YC-Backed Startups Reveal About the Future of Tech & AI
Decoding YCombinator's Latest Cohorts
82% of YC's latest startups are AI-focused. Yet most founders are still building in overcrowded spaces, missing massive opportunities in untapped markets.
Six months ago, my analysis of YC's previous cohorts helped many people spot emerging trends.
This time again, I've analyzed 400 companies from YC's last three cohorts to decode what gets funded in 2025.
The patterns are striking: while 144 companies build AI agents, only one targets last-mile delivery—a $200B market.
Here’s what this analysis gives you:
Spot Emerging Trends: See which industries, technologies, and business models YC is betting on in 2025 and beyond.
Avoid Oversaturated Markets: Learn which AI verticals are crowded (like AI agents) and where the untapped opportunities lie (like last-mile delivery).
Validate Your Startup Idea: Find out what problems YC-backed startups are solving—and where you can carve out your niche.
Understand YC’s Priorities: Discover why 82% of funded startups are AI-focused and why B2B dominates the landscape.
Access Actionable Data: Get a clean, structured CSV file to run your own analysis and make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Whether you're applying to YC or building the next big thing, this report will help you spot opportunities others miss. Let's dive into what works.
Key findings upfront:
82% are AI companies, signaling YC's clear priority
69% target B2B, showing enterprise is where the money flows
SF Bay Area houses 62%, but remote teams are rising
Let's dive into the data and find your winning strategy.
Data
I collected the data from YC’s Startup directory for latest startups that got accepted in the Summer 23, Fall 24, Winter 25 cohorts.
The data required cleaning and some transformations to extract the tags they have and rechecked it from the description of the company to capture their main category.
I got 396 companies in the data with their description, urls, tags / categories, active founders, and founders’ bio.
If you need this data for your own analysis, you can get your copy from here.
While looking at a subset of these companies, I have found many exceptional use cases of AI.
Now, let's unpack what's working in YC.
⚠️ Disclaimer: Some parts of this report is generated with the help of LLMs and the numbers are approximate.
AI vs Non-AI
AI isn’t the future—it’s the present.
At this point, there are only 2 types of companies, ones that are building around AI and others that are not.
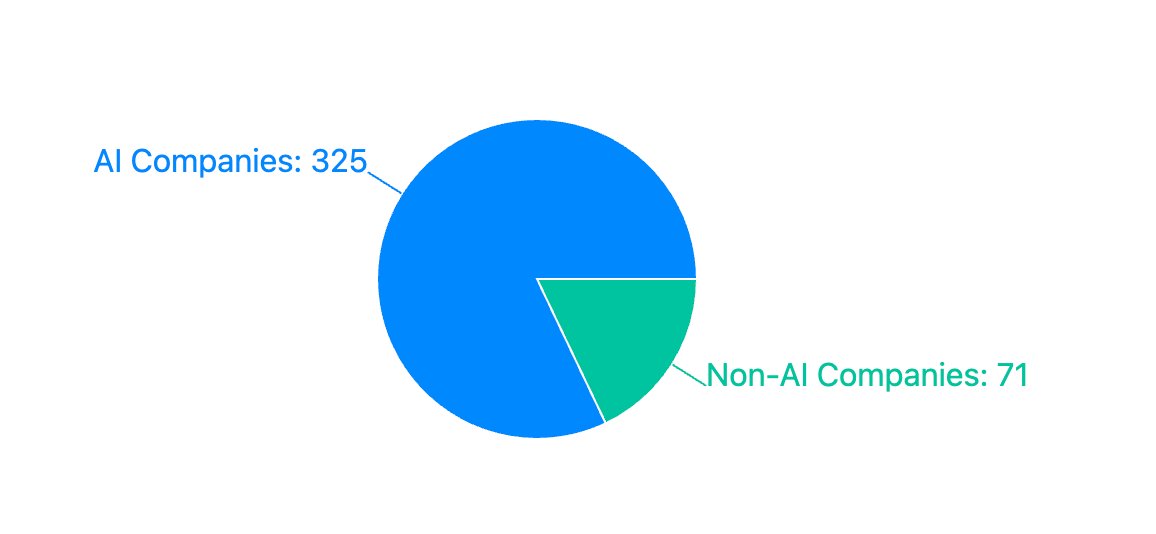
82% (325) of YC-accepted companies in the last 3 cohorts are AI-focused.
Non-AI startups are a declining minority with only 18% (71) companies getting accepted.
A strong data point for anyone planning to apply for YCombinator’s newly announced Spring cohort. This shows they are inclined to accept more applications from AI companies.
Having established AI’s dominance, we explore how business models (B2B vs B2C) shape startup strategies.
B2B vs B2C
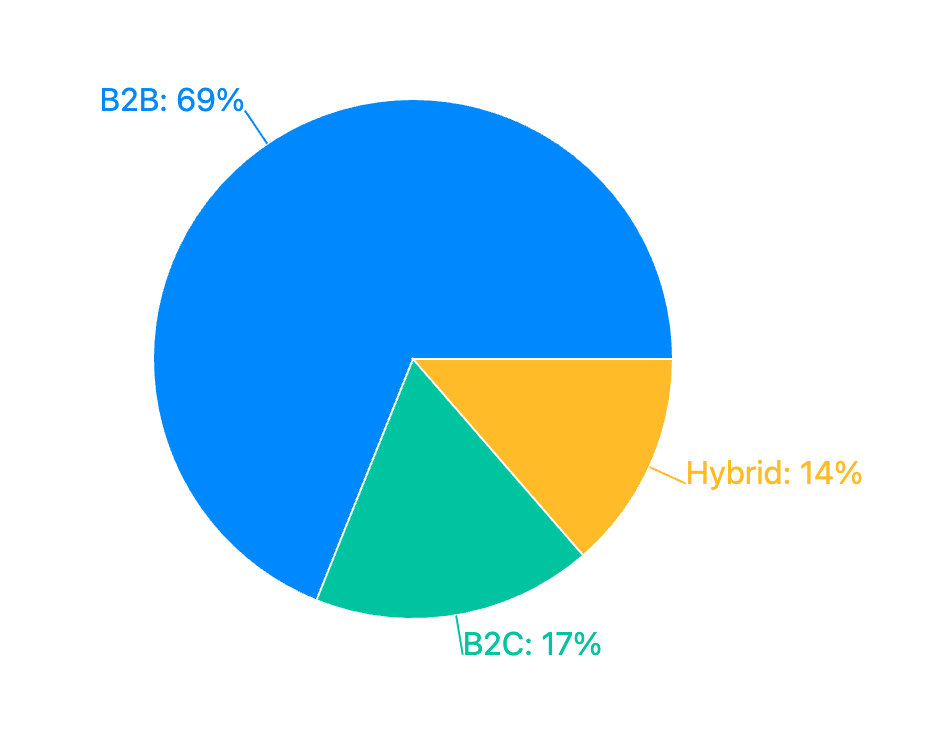
69% (273) of startups target enterprises and developers, like Tabular (accounting automation) and Mem0 (LLM tools).
Just 17% (69) focus on consumers, with apps like pap! (personal finance) and BeeBettor (sports betting).
B2B (273 companies, 69% of total) Dominant Verticals:
Developer Infrastructure:
Tools for AI development (e.g., Mem0's LLM memory layer)
Security solutions (e.g., ZeroPath's vulnerability detection)
Data infrastructure platforms
Enterprise Software:
Workflow automation (e.g., Tabular's accounting automation)
Business intelligence and analytics
Compliance and risk management
Industry-Specific Solutions:
Healthcare providers
Financial institutions
Manufacturing optimization
B2C (69 companies, 17% of total) Dominant Verticals:
Personal Finance:
Money-saving tools (e.g., pap!'s automated savings)
Investment platforms
Personal financial management
Consumer Apps:
Productivity tools
Entertainment (e.g., BeeBettor)
Personal wellness
Consumer Services:
Healthcare services
Educational tools
Lifestyle management
Hybrid (54 companies, 14% of total) Common Patterns:
Marketplace Models:
Connecting businesses with consumers
Two-sided platforms
Shared economy solutions
Multi-stakeholder Platforms:
Healthcare platforms (serving both providers and patients)
Educational platforms (serving institutions and students)
Real estate platforms (serving agents and buyers)
Key Trends and Insights:
AI Adoption Patterns:
B2B leads in overall adoption (83%)
Hybrid models show highest AI adoption (87%)
B2C shows lowest but still significant adoption (74%)
Investment Focus:
Heavy concentration in B2B (69% of companies)
Suggests stronger monetization potential in enterprise market
Higher barriers to entry in consumer market
Market Opportunity Signals: B2B Opportunities:
Infrastructure for AI deployment
Vertical-specific AI solutions
Enterprise automation platforms
YC prioritizes B2B startups with clear enterprise monetization paths—critical for founders eyeing the Spring cohort.
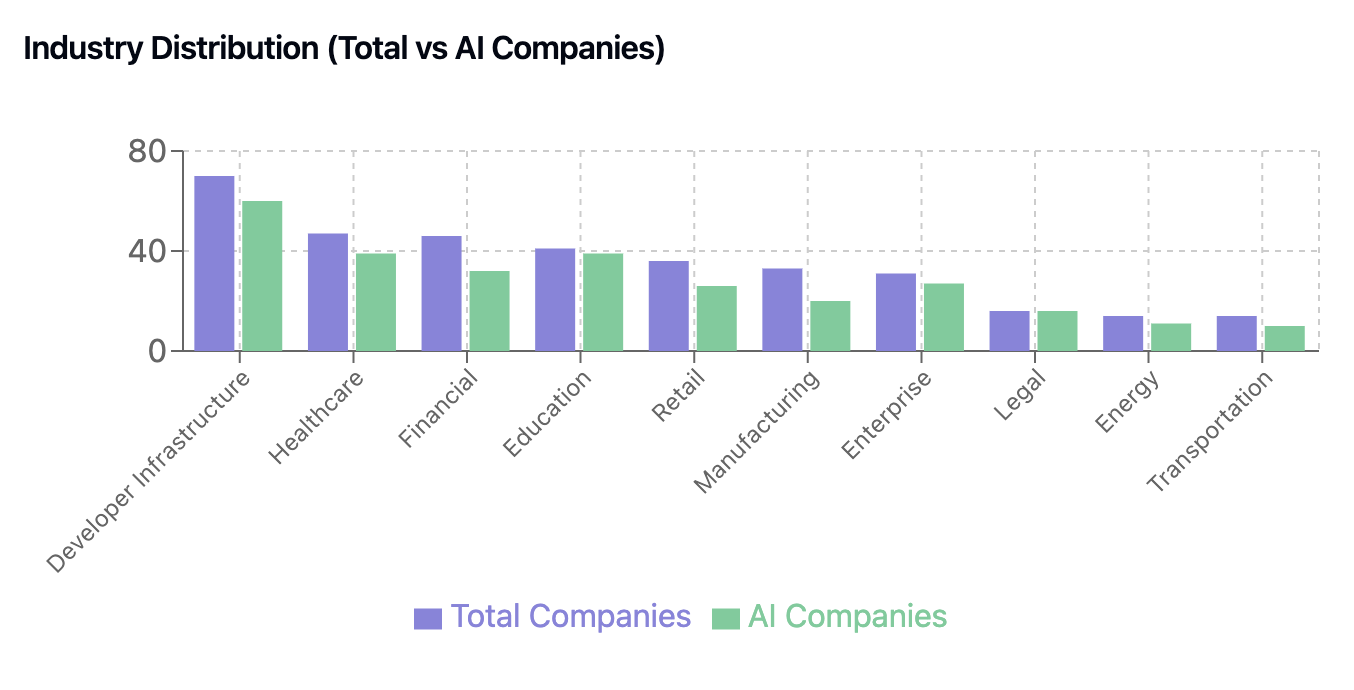
Industry Breakdown: Sector-Specific AI Transformation
1. Developer Infrastructure (70 companies)
86% of the YC-accepted dev infra companies are building around AI.
Focus: Development tools, cloud infrastructure, DevOps.
Example:
2. Healthcare (47 companies)
83% of these 47 companies are solving problems with AI.
Focus: Clinical trials, drug discovery, medical billing.
Example:
3. Financial Services (46 companies)
70% these startups are automating processes for businesses with AI.
Focus: Accounting, payments, insurance
Example:
4. Education (41 companies)
95% of the education companies are AI companies.
Focus: Personalized learning, content generation
Example:
Capitol AI - Custom search and content platform
Edexia - AI teaching assistant that learns individual teacher grading styles
5. Retail (36 companies)
72% are AI companies.
Focus: E-commerce, consumer experience, product visualization
Example:
Key Patterns from Industry Distribution:
AI Adoption by Sector
Leaders: Legal (100%), Education (95%), and Media (91%)—loosely regulated sectors that are embracing AI for efficiency.
Laggards: Manufacturing (61%) and Agriculture (50%)—complex workflows and slower tech adoption.
Average Penetration: ~80%, signaling AI’s broad-based integration across industries.
2. Dominant Industry Focus
Infrastructure & Tooling: Largest sector, driven by demand for AI development frameworks.
Healthcare & Financial Services: Strong traction due to high-value use cases (e.g., clinical trials, fraud detection).
Climate Tech: Emerging hotspot, with AI optimizing energy and sustainability workflows.
3. Business Model Shifts
B2B Dominance: Enterprise solutions rule, targeting workflow automation (e.g., compliance, accounting).
Vertical Specialization: Surge in industry-specific AI tools (e.g., legal document automation, medical billing).
4. Innovation Frontiers
Traditional Industries Reborn: Legal and healthcare sectors reinvented via AI-driven efficiency (e.g., automated compliance, drug discovery).
Infrastructure Buildout: New tools for deploying AI at scale (e.g., LLM memory layers, cloud infrastructure).
Domain Expertise + AI: Convergence creating defensible moats (e.g., AI-powered mining optimization, agricultural yield analytics).
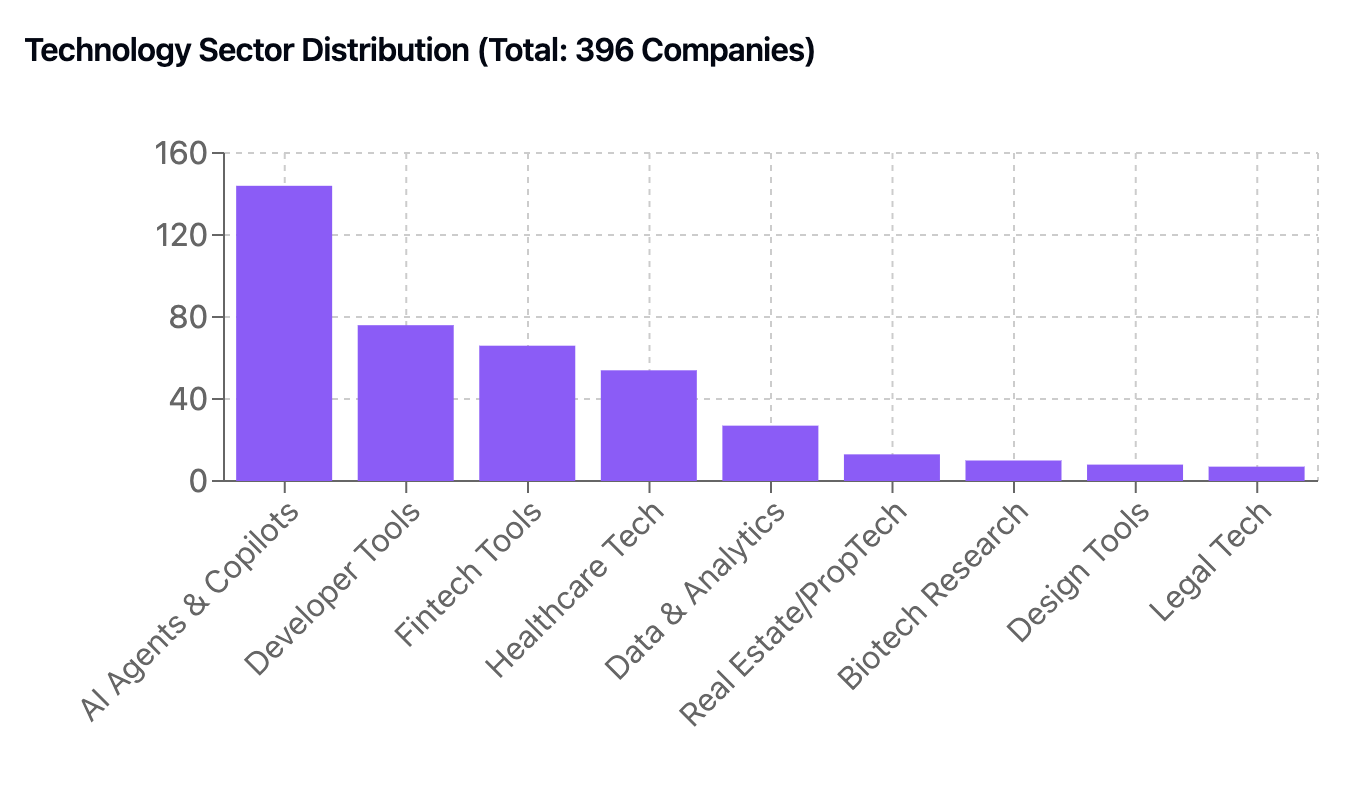
Technology Sector Distribution
AI Agents & Copilots (144 companies, 36.4%)
Focus Areas:
Business process automation (e.g., Tabular)
Consumer automation (e.g., pap!)
Industry-specific assistants (e.g., Plume)
→ Crowded Space: Highest competition but massive market opportunity. Strong potential for specialized solutions.
Developer Tools & Infrastructure (76 companies, 19.2%)
Focus Areas:
LLM development tools (e.g., Mem0)
Code security (e.g., ZeroPath)
AI infrastructure (e.g., Lumen Orbit)
→ Highest Competition density: Strong focus on AI development tools and infrastructure.
Fintech Tools (66 companies, 16.7%)
Focus Areas:
Compliance automation (e.g., Focal)
Investment analytics (e.g., Bayesline)
Insurance tech (e.g., SureBright)
→ Mature: Well-funded competitors with established products.
Healthcare Tech (54 companies, 13.6%)
Focus Areas:
Clinical documentation (e.g., Baseline AI)
Medical billing (e.g., Taxo)
Health records analysis (e.g., RiskAngle)
→ Growing: Significant regulatory barriers but high potential.
Data & Analytics (27 companies, 6.8%)
Focus Areas:
Business intelligence
Process analytics
Performance monitoring
→ Competitive: Especially in enterprise data analysis.
Emerging Technology Sectors:
Real Estate/PropTech (13 companies, 3.3%)
Underserved market
Complex workflows
High value transactions
Biotech Research (10 companies, 2.5%)
High barriers to entry
Significant technical requirements
Large market potential
Design Tools (8 companies, 2.0%)
Creative AI applications
Visual content generation
Design automation
Legal Tech (7 companies, 1.8%)
Wide-open opportunity
High regulatory complexity
Large market potential
The number of startups building around AI Agents is living upto the hype. As many people are claiming that 2025 is the year of AI Agents, here’s a deep-dive on AI Agents companies.
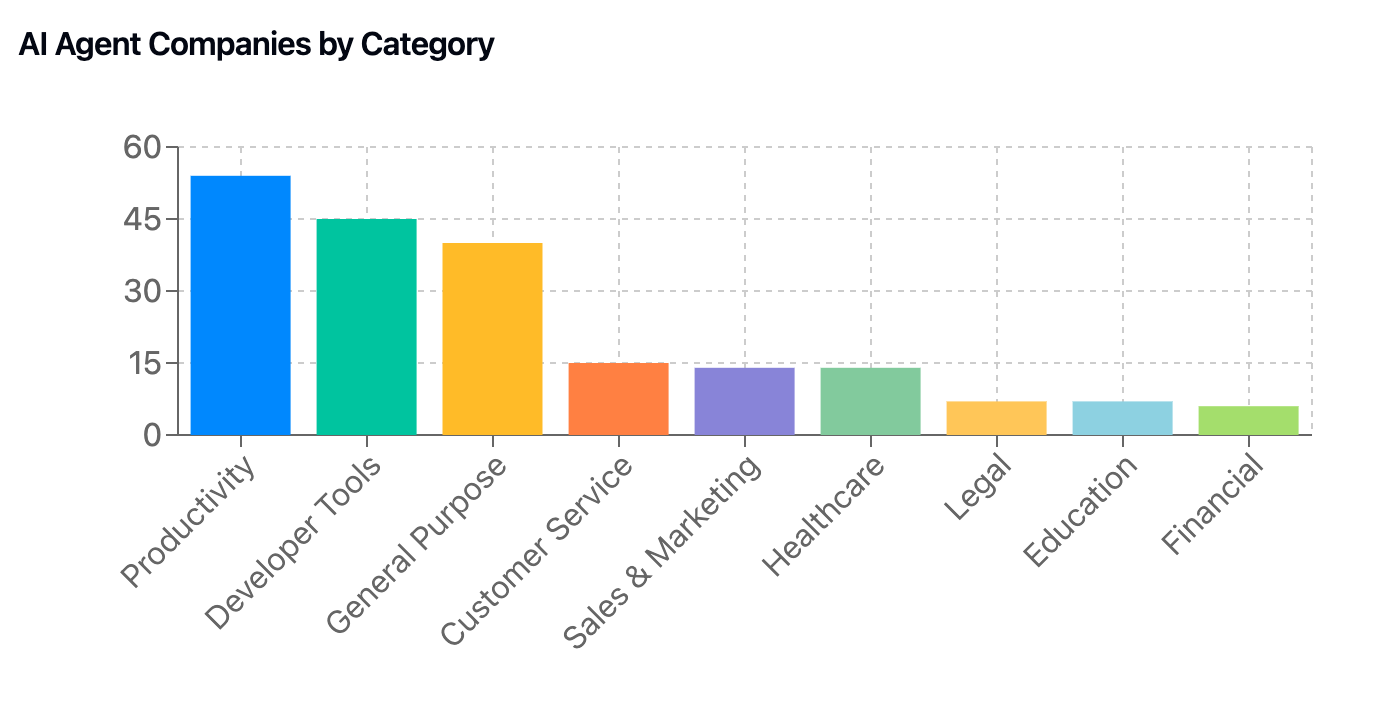
Detailed breakdown of AI Agent companies
Productivity Agents (54 companies, 27%) Key Focus Areas:
Document Processing (e.g., Tabular - accounting automation)
Workflow Automation (e.g., Poka Labs - manufacturing operations)
Task Management (e.g., Ceejay - AI executive assistant)
Developer Tools (45 companies, 22%) Key Focus Areas:
Code Generation (e.g., Mem0 - LLM memory layer)
Security (e.g., ZeroPath - vulnerability detection)
DevOps (e.g., Kura - cloud infrastructure management)
General Purpose Agents (40 companies, 20%) Key Focus Areas:
Multi-modal Interaction (e.g., Kura AI - web interaction)
Task Automation (e.g., SureBright - warranty automation)
Cross-domain Solutions (e.g., Plume - energy assessments)
Customer Service (15 companies, 7%) Key Focus Areas:
Support Automation (e.g., Parahelp - ticket resolution)
Voice Agents (e.g., Phonely - call center automation)
Customer Success (e.g., Canvas - customer success copilot)
Sales & Marketing (14 companies, 7%) Key Focus Areas:
Lead Generation (e.g., OpenFunnel - B2B prospecting)
Market Research (e.g., Conveo - qualitative research)
Sales Automation (e.g., telli - voice sales agents)
Healthcare (14 companies, 7%) Key Focus Areas:
Clinical Support (e.g., Vera Health - decision support)
Patient Operations (e.g., ShowAndTell - dental patient ops)
Medical Documentation (e.g., Ember Copilot - medical scribe)
Legal (7 companies, 3%) Key Focus Areas:
Compliance (e.g., Sphinx - AML automation)
Documentation (e.g., Fresco - construction notes)
Risk Assessment (e.g., Praxos - insurance operations)
Education (7 companies, 3%) Key Focus Areas:
Grading (e.g., GradeWiz - assignment grading)
Tutoring (e.g., ISSEN - language learning)
Educational Content (e.g., MinusX - data science education)
Financial (6 companies, 3%) Key Focus Areas:
Investment Analysis (e.g., Decisional AI - private markets)
Real Estate (e.g., Henry - CRE broker copilot)
Fraud Detection (e.g., Rulebase - fraud investigation)
Open Source vs Proprietary
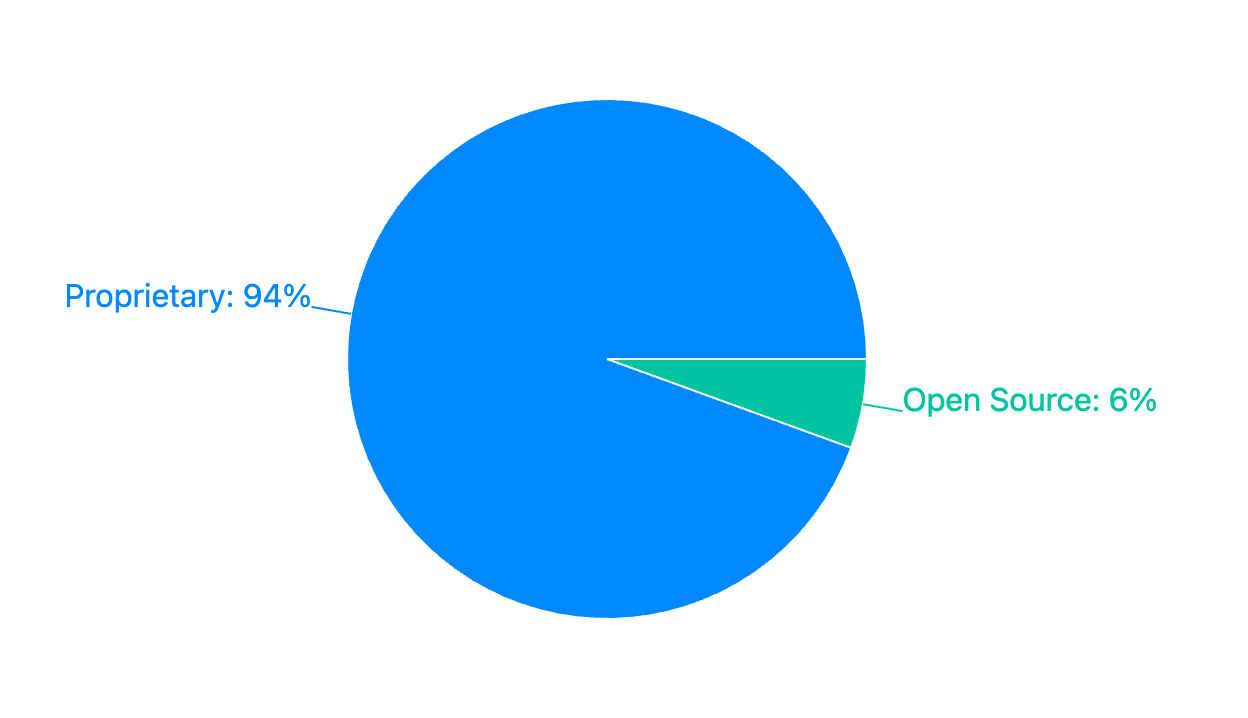
1. Overall Distribution
Open Source: 22 companies (5.6% of total)
AI Companies: 16 (73% of open source)
Non-AI Companies: 6 (27% of open source)
Proprietary: 374 companies (94.4% of total)
AI Companies: 309 (83% of proprietary)
Non-AI Companies: 65 (17% of proprietary)
2. Open Source Focus Areas
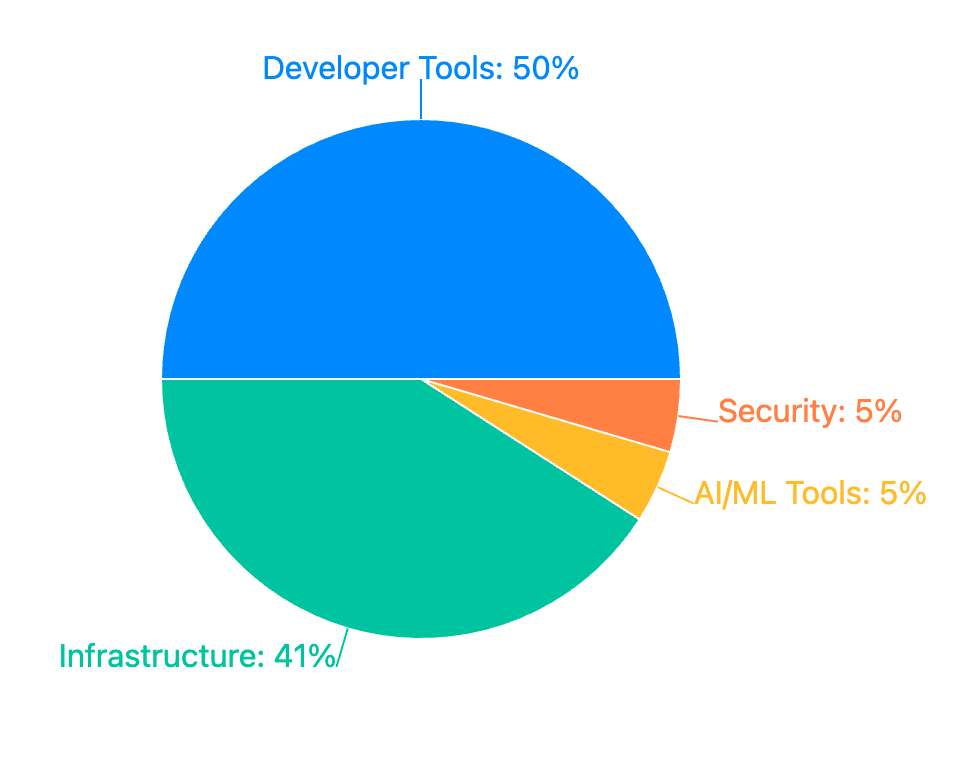
a. Developer Tools (50% of open source companies)
Example: Random Labs - open source software agents
Focus: Development frameworks, IDEs, coding tools
Key Trend: Strong emphasis on developer experience
b. Infrastructure (41% of open source companies)
Example: Mem0 - LLM memory layer
Focus: Cloud infrastructure, deployment tools
Key Trend: Building foundational AI infrastructure
c. AI/ML Tools & Security (5% each)
Limited but growing presence
Focus on core AI capabilities
Emphasis on transparency and community involvement
Most Common Problems Companies Are Solving:
1. Efficiency (50 companies) Problem: Slow, inefficient processes that create bottlenecks
Examples:
Taxo: Reduces medical billing processing time by 90%
Synnax: Accelerates hardware evaluation and testing
Mem0: Speeds up LLM application response times Key Pattern: Focus on reducing time-to-completion for critical business processes
2. Cost Reduction (35 companies): Expensive manual operations and resource-intensive processes
Examples:
RetroFix AI: Saves hundreds of thousands in tax incentives
Pharos: Saves millions in labor costs for hospitals
Focal: Reduces compliance operation costs for banks Key Pattern: Targeting high-cost business functions with AI automation
3. Manual work automation (31 companies): Repetitive, time-consuming tasks that require human attention
Examples:
Dodo: Automates veterinary clinic front/back office tasks
Focal: Automates compliance workflows
RetroFix AI: Automates tax incentive applications Key Pattern: Replacing routine human tasks with AI agents
Common Threads Across All Three Problems:
Focus on Business Operations:
Most solutions target internal business processes
Strong emphasis on B2B applications
High concentration in regulated industries
Value Proposition:
Time savings (efficiency)
Cost reduction
Error reduction
Resource optimization
Implementation Approach:
AI-powered automation
Integration with existing systems
Focus on specific industry verticals
Automation is the dominant theme, appearing in 104 companies' descriptions. The core concept across companies is "automating manual, time-consuming processes using AI."
Moving away from the common themes, let’s zoom into the moonshot territories where startups aren’t just iterating—they’re rewriting the rules of what’s possible. From AI-powered satellites to bioengineered microbes, here’s how founders are blending cutting-edge tech with industries you’d least expect.
Distribution of Emerging Technology Companies
1. Space Tech (19 Companies)
AI Adoption: 63%
Key Players:
Lumen Orbit: Space-based data centers for AI training, leveraging passive cooling and energy efficiency.
Others: AI-powered satellite operations, Earth observation analytics.
Trends:
Growth in space-based computing infrastructure.
Focus on solving energy and cooling challenges for AI workloads.
2. Advanced Robotics (17 Companies)
AI Adoption: 59%
Key Players:
Cerulion: Open-source robot OS used by Amazon Robotics and Boston Dynamics.
Azalea Robotics: Automates airport baggage handling ($20B+ market).
Trends:
Enterprise-focused automation (logistics, manufacturing).
Strong demand for intelligent, scalable robotic systems.
3. Synthetic Biology (14 Companies)
AI Adoption: 57%
Key Players:
1849 bio: Bioengineered microbes for sustainable mining.
Evolvere Bio: Next-gen antibiotics targeting drug-resistant bacteria.
Trends:
AI-driven biomining and drug discovery.
Applications in climate tech and healthcare.
4. Blockchain/Crypto (4 Companies)
AI Adoption: 0%
Key Players:
Blaze: USDC-based cross-border payments.
Karsa: Stablecoin marketplace for inflation-hit markets.
Trends:
Focus on financial inclusion in emerging markets.
Gap: No integration with AI/ML tools.
5. Quantum & Edge Computing (2 Companies)
Quantum Computing (1):
Conductor Quantum: AI-integrated quantum chips for computational breakthroughs.
Edge Computing (1):
Keye: Real-time data analysis for private equity due diligence.
Trends:
Early-stage innovation with high technical barriers.
Gaps & Opportunities
Untapped Potential:
Blockchain + AI: No startup from these cohorts merge decentralized systems with AI (e.g., fraud detection, DeFi analytics).
Quantum Computing: Only 1 player—room for quantum-AI hybrid models.
Investment Hotspots:
Space-AI Infrastructure: Energy-efficient orbital data centers.
Biotech-Industrial Crossover: Mining, agriculture, and pharma applications.
Robotics-as-a-Service: Scalable automation for logistics and healthcare.
Enough about AI companies, not falling for the hype are some very interesting startups. Here is what I found while looking into the industries Non-AI companies are targeting.
Industries / Sectors that Non-AI Companies are targeting
B2B/Enterprise (17 companies, 33.3%)
Examples:
Fortress (database platform) - Postgres developer platform that makes it simple to globally distribute data.
Tandem (office marketplace) - Marketplace to help companies lease and share office space.
Technology: Traditional software, databases.
Developer Tools (17 companies, 33.3%)
Examples:
Glasskube (Distribution platform) - Software Distribution Platform for on-prem and air-gapped customers.
Synnax (Hardware evaluation) - Sensor data processing
Technology: Database systems, Infrastructure, API integrations
Fintech (11 companies, 21.6%)
Examples:
CardLift (credit card optimization) - Rules-based workflows
Central (back-office) - Programmatic workflows
Technology: API integrations, workflow engines
Healthcare (8 companies, 15.7%)
Examples:
Evolvere BioSciences (antibiotics) - Traditional biotech
Durate (hospital scheduling) - Rule-based scheduling
Technology: Traditional software, scheduling algorithms
E-commerce (4 companies, 7.8%)
Examples:
Clara (caregiver marketplace) - Traditional marketplace
Tandem (office space) - Listing platform
Technology: Database-driven platforms
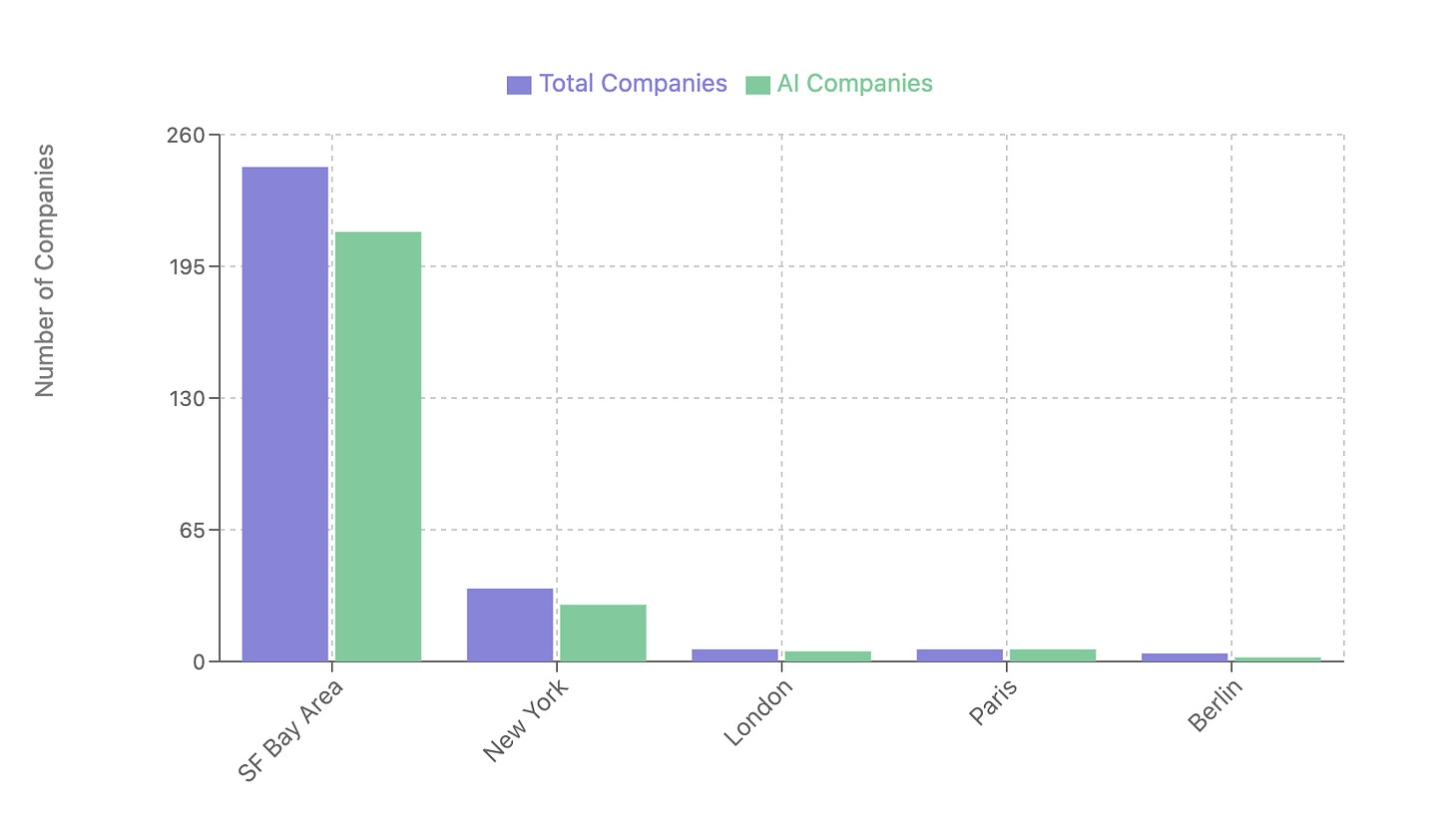
Geographic Distribution of Accepted Companies
Geographic Concentration:
SF Bay Area dominance (62% of companies)
Strong East Coast presence (10%)
Growing European ecosystem (4%)
No surprise here!
Since most of the top league AI companies, YCombinator themselves and startups / tech communities are based in San Fransisco and given their focus on AI technologies, a large majority of teams getting selected are based out of SF.
This doesn’t mean if you’re trying to apply from anywhere outside of SF, it is going to be held against you. As long as your business is solid and solves real problems, you can get through.
It’s just that people in SF do have an edge as they are surrounded by top players in AI and that’s where the wind is blowing.
More questions?
I can continue getting answers to all sorts of questions from this data but you’d get more interesting specifics based on your curiosity.
Here are some thought provoking questions that I got:
Market Opportunity Questions:
With 17 logistics startups, why is only 1 focusing on last-mile delivery ($200B market)?
Just 2 agriculture startups in a vital global sector - what's blocking innovation here?
Growth Strategy:
71 Non-AI companies got accepted - what's their competitive advantage?
Why are only 21 companies in Healthcare AI despite massive market size?
Only 10 edtech startups - is education too regulated or undervalued?
Summary
1. AI Dominance: 82% (325) of YC companies are AI-focused, with only 18% (71) non-AI companies, showing strong preference for AI startups.
2. Business Model Distribution: 69% (273) are B2B, 17% (69) B2C, and 14% (54) hybrid models, indicating strong enterprise focus.
3. Technology Sectors: AI Agents lead (36.4%, 144 companies), followed by Developer Tools (19.2%, 76), Fintech (16.7%, 66), and Healthcare (13.6%, 54).
4. Team Structure: 77% have 2-3 founders, with average team size of 2.8, suggesting optimal small team composition.
5. Geographic Concentration: 61.6% based in SF Bay Area, 10% East Coast, 4% Europe, showing continued Silicon Valley dominance.
6. Emerging Technologies: Notable presence in Space Tech (19 companies), Advanced Robotics (17), and Synthetic Biology (14), with limited blockchain/crypto (4) and quantum computing (2) representation.
7. Notable Gaps: Limited presence in construction tech (6 companies), agriculture (2), and last-mile delivery (1) despite large market sizes.